Differential type flow measurement are employed in many industries like chemical and petrochemical plants, Refineries, water treatment plants etc.Flow measurement using primary elements like orifice plate ,venturi tube ,pitot tube etc are examples of head pressure method of flow measurement .These primary elements are flow restrictions which creates a Differential pressure in the flow stream . Differential pressure varies with flow rate..In this method Dp press created by these primary sensing elements is measured using a differential pressure transmitter .And this measured differential pressure value is converted to flow rate . The Differential pressure and flow conversion can be done easily if we know the know the their relation and concepts . Differential pressure dp and flow calculations ,This article describes the relationship between differential pressure and flow ,the concepts , conversion with some examples etc .
Linear and Square root relationship
Linear Relationship
Most of the measurement techniques employed in industries to measure various parameters like flow, level ,temperature etc possess linear behavior between the primary variables and the variables which we need to measure.
For example level measurements using DP transmitter, pressure measurement using pressure transmitter, temperature measurement using RTD , flow measurements using magnetic flow meter etc.In all these devices their output keeps linear behaviour with the variable .
In level measurement using Dp transmitter , the level and differential pressure keeps linear relationship with each other.
We can say level L= k×DP
Another example.In flowmeters like Magnetic flowmeter , coriolis flow meter ultrasonic flow meter ,etc keeps linear relationship with its sensed signal.The millivolts reading in magnetic flowmeter keeps linear relationship with flow .If we plot them on x,y axis we will get a straight line. A 25% signal will reads as flow as 25% ,and a 50% of full range signal will interpret flow as 50% of full range and so on.see above figure. It
Square root relationship
SQUARE ROOT CHARACTERISTICS
Differential pressure type flow instruments like Dp transmitter keeps square root relationship with flow. The measured DP has no linear relationship with flow .In hydrostatic type flow measurement, differential pressure and flow related as,
F = k√DP
So 25% of Dp full range is not corresponds to 25% of full range of flow!!!!!!!when Dp is 25% flow is 50% when Dp is 50% flow is 70.9%…etc.If we plot Dp and flow on x and y axis respectively, then we will get a parabolic curve.
The below figure shows the variation of flow with Differential pressure.Note that the curve is not straight line. Or the relationship between flow and dp is not linear . We can see from the below figure that it is parabolic in nature .
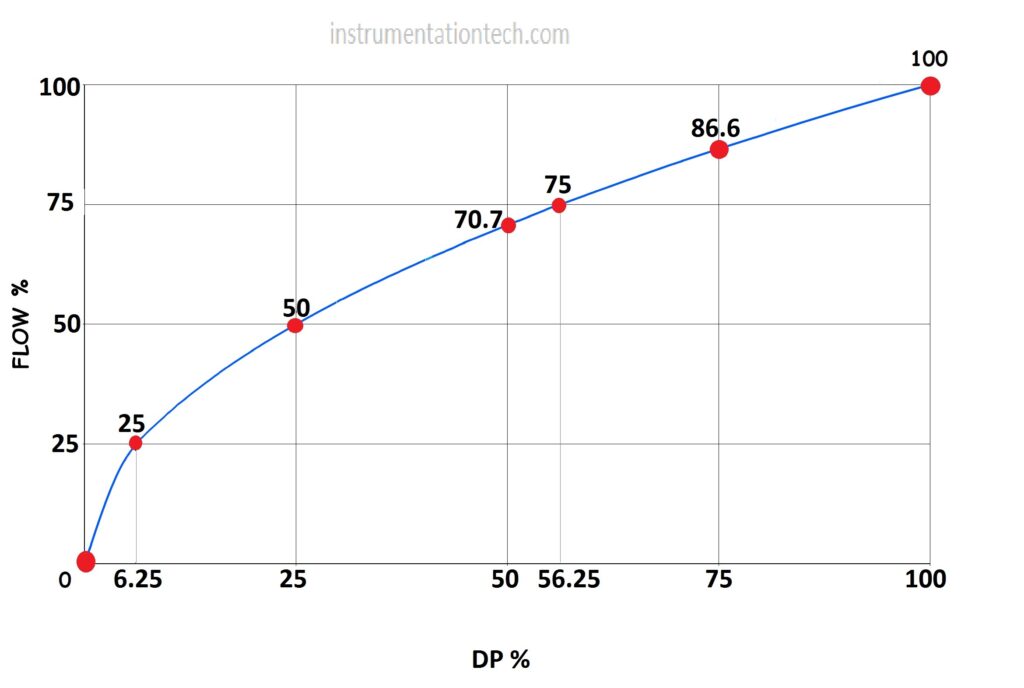
F=k √Dp
Where F= flow
Dp= Differential pressure
The constant k depends on factors like viscosity, density etc.
In instrumentation systems for flow measurement,using DP transmitter,the measured Dp has to be converted in to flow.In linear measurement systems it is easy to corelate the variables with the sensed signal .But in this case a mathematical function called square root extraction is needed.Square root extraction means applying square root on dp to get flow.
Where to employ square root extraction?
Where will we employ these square root extraction function ???
In control room side ???
or field side?
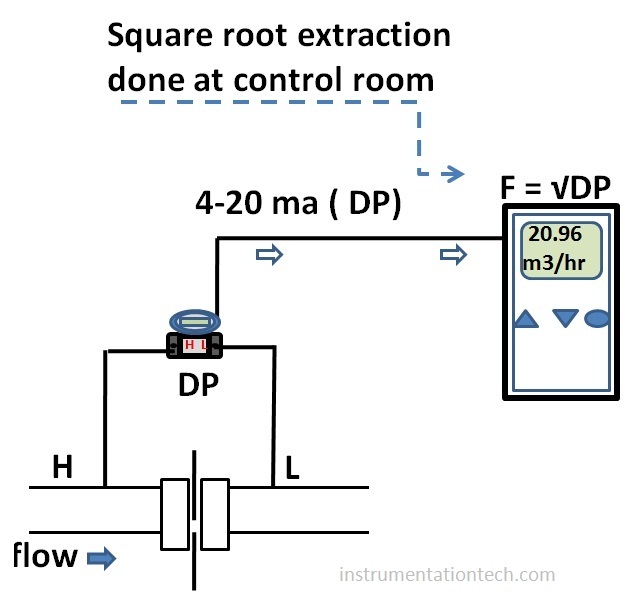
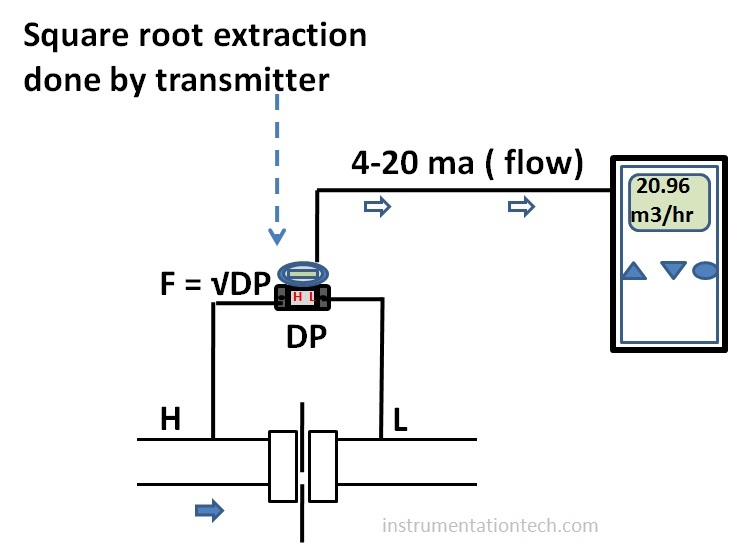
We can do this function in control room side( PLC or DCS) or We can do it in DP transmitter also as modern transmitter are capable for doing the square root extraction calculations and transmitt a signal proportional to flow . It is important to ensure square root extraction has done and only at one side.
In this article we are focussing on the flow related calculations . when we are given data like flow range, Differential pressure etc .
Differential pressure and flow conversion
Note
In percentage calculation we don’t need the factor k ,so we can avoid the factor k when we are calculating flow% or Dp% .
So in our problems to find DP and flow in % we use equation as
FLOW= √DP
DP= (FLOW) 2
Differential pressure and flow conversion /percentage calculations .
To find flow% when DP% is given
Dp=0%. What is flow?
Ans: Flow = √dp
= √0%
= 0%
DP is 25% what is flow?
F = √dp
= √25% ( 25%means 25/100 )
=√25/√100
=5/10
=50/100
=50%
DP is 50% what is flow?
F = √dp
= √50%
=√50/√100
=7.071/10
=70.71/100
=70.71%
To find DP% when flow % is given
Flow is 25 % what is DP
Given Dp=25%. Means 25/100
Dp=(FLOW) 2
= (25/100)2
= 6.25/100
= 6.25%
Flow is 50 % what is DP
Given Dp=50%. Means 50/100
Dp= (FLOW) 2
= (50/100)2
= 25/100
= 25 %
Flow is 75 % what is DP
Given Dp=75%. Means 75/100
Dp=(FLOW) 2
= (75/100)2
= 56.25/100
= 56.25 %
Flow is 100 % what is DP
Given Dp = 100 %. Means 100/100
Dp = (FLOW) 2
= (100/100)2
= 100 %
Differential pressure and flow conversion when actual range is given .
Suppose we have a DP transmitter calibrated for a flow range.we know the equation holds good throughout the range
For flow1 we have DP1 so we can write as
Flow1=k√DP1
and for Flow2 we haveDP2
So we can write it as.
Flow2 =k√DP2
eqn1÷2 gives
Flow1/Flow2 = √DP1/√DP2
Example 1
A Dp transmitter is used for flow measurement through a pipeline .Dp transmitter is calibrated to 0-5000mmwc for a flow range of 0- 250m³/hr.
Find the flow rate when the transmitter senses a differential pressure of 3100 mm wc.
Flow =k √dp
Flow1/flow2 =√DP1/√DP2
250/flow2=√5000/√3100
Flow2 =250×√3100/√5000
=197m³/Hr
Flow rate when DP is 3100mmwc is 197 m³/Hr
EX: A DP transmitter which has range 0-3000mmwc for 0-240m³/hr flow .
what is the DP when flow =190m³/hr
Ans
For flow=240m³/hr. DP=3000mmwc
240= k√3000
When flow =190m³/HR,
190 =k√DP2
Eqn2÷eqn1 gives
190/240 =√DP2/√3000
DP2=190²×3000/240²
=1880 mmwc
Differential pressure and flow conversion .calculations involving output milli ampere
Example 2
what is the flow rate when the output of a DP transmiter is 14 ma . square root conversion is done at control room side.The flow range is 0- 400m³/Hr.
Ans: square root conversion is done at control room.so the output is proportional to DP
DP(ma) Flow
20ma…………………..400 m³/HR
14ma…………………..F ?????
√(20-4) / √(14-4) = 400/F ****
F = 400×√10/√16
= 316 m³/hr
(**** we substract 4 mA because the signal 4-20 ma has It’s zero is shifted by 4ma from zero .)
Example 3
transmiter is doing Square root conversion,and all tha data are same as the previous question.Then what will be the flow when output current of 14 ma.
Ans: Here transmiter already done square root conversion and the milliamps signal corresponds to flow .we don’t want further square root conversion. The signal is linear with flow
So ,Flow when current is 14ma ,
Taking linear relation
Flow.(m³/Hr) Flow (ma)
400. ………………….20ma?
?? F…………………..14 ma
400/F =(20-4) /(14 -4)
F=(14-4)×400/16
= 250 m³/hr
Example 4
What is the output current of transmiter when flow =300m³/HR.square root conversion done at control room. Flow range0-400m³/Hr
ANS: Here ma corresponds to DP. we need to employ square root relation.
Flow…………………. (DP) mA
400……………………20 ma
300 ……………………..???? ma
400/300 =√ (20-4) / √(mA-4). ****
(400/300)² =16 /(mA-4)
ma = 4 + [16 / (400/300)²]
=13 mA
(**** we substract 4 mA because the signal 4-20 ma has It’s zero is shifted by 4ma from zero .)
online converter for flow and differential pressure
Try the online converter to get flow or differential pressure instantly.See below .