Thermocouples are sensors used for temperature measurement .They works on the principles of thermoelectric effect .They are constructed as a couple or junction of two different metals .They generates an emf due to the thermoelectric difference between the metal junctions kept at two different temperatures.
Seebeck effect
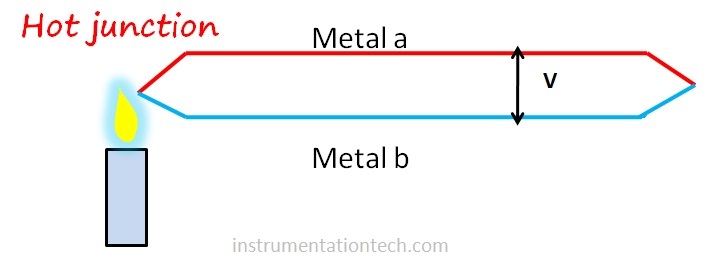
If two metals with dissimilar electrical properties are joined at both ends and one end made hot an emf is generated between the two metals which is proportional to the difference in temperature between the two junctions. seebeck discovered this and it is called seebeck effect.
This is the basic principle behind temperature measurement using thermocouples. They are widely used in process instrumentation for temperature control and temperature monitoring applications ..

Thermocouple construction
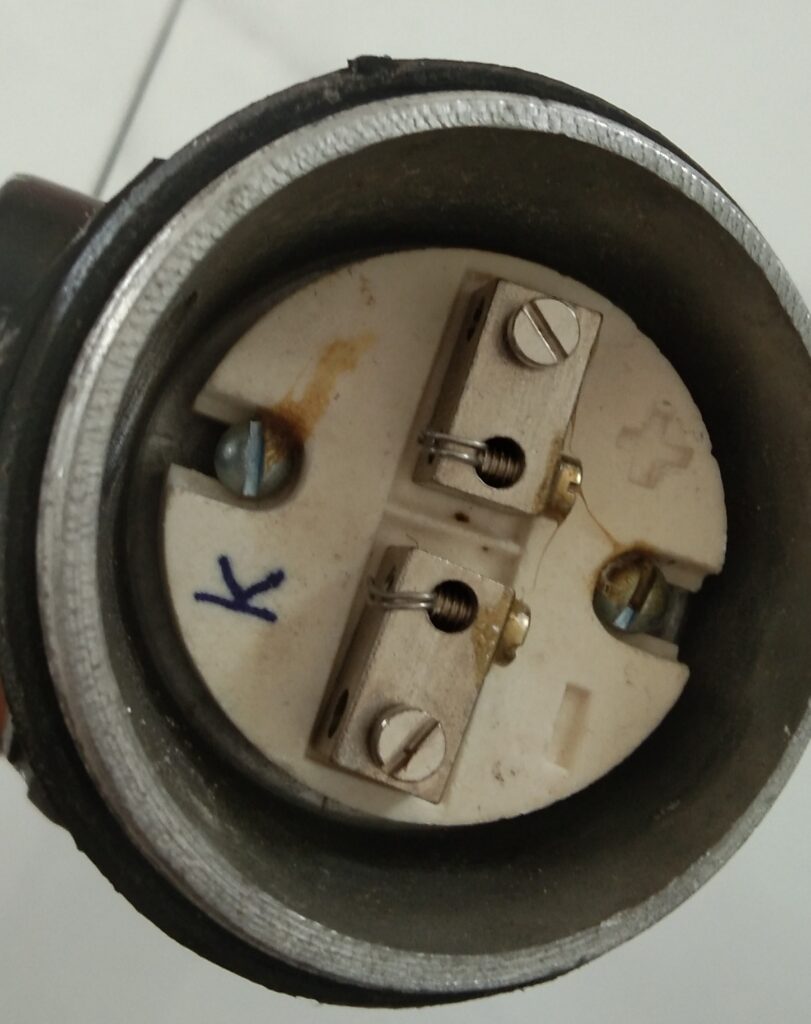
Thermocouples consist of two metal wires made from different metals. They are welded together at one end, creating a junction called hot junction .The metal wires are properly insulated from each other by means of ceramic powder or beads . Also protective sheaths are provided in most cases . Terminals for connecting extension wires are provided .This whole unit is properly installed in the process connection point .
The unit is connected to the receiving instrument ( indicator, controller,thermocouple modules etc) through proper compensating wires.The receiving junction or reference junction is also called cold junction.The temperature gradient causes a potential difference to develope between them .These potential difference corresponds to the temperature difference .By knowing the temperature at the reference junction we can determine the temperature at the hot junction .
Types
Many types of Thermocouples are available in industry. These types are defined based on the metal or alloy combination used . Each type has its own range of measurement , environmental compatibility,range of millivolts output etc .Some of them are given below.
K. chromel – Alumel. 0 -1260°C
J iron – Constantan 0 -760°C
R. platinum – Platinum Rhodium(13%)
S. platinum – Platinum Rhodium(10%)
T Copper constantan -200 – 370°C
Reference junction compensation
The voltage produced by thermocouple is due to the difference in temperature between hot junction and cold junction.Actually this voltage tells the temperature difference.For example a 13.6mv measured at the cold junction of a K type thermocouple. This data gives us what?
On seeing thermocouple tables this voltage corresponds to 800°C.Does that mean the hot junction is at 800°C???
No….
It means the Difference in temperature between hot junction and cold junction is 800°CThe following shows some possibilities.
Hot jn Cold jn
840 40
830 30
820 20
In all of the above situations we will get same millivolts signal.This is because the temperature difference is same in all situations(800°C ) represented above .The fact is Thermocouple only see the temperature difference between the hot and cold junctions .
The temperature at hot junction is different in all these situations .But our aim is to detect the temperature at the process (Hot junction)
So to know the temperature at the hot junction, we should know the temperature at the reference junction and compensate for this temperature in measurement circuit .This is achieved through measuring the temperature in the cold junction with another sensor usually RTD or thermistor and adding compensations in the measuring circuit in accordance with this temperature .This process is called reference junction compensation or cold junction compensation .


Thermocouple charts
Each types of thermocouple shows different variations in millivolt with the temperature variations. Tables were constructed for each one indicating millivolts at each temperature values .Tables prepared assuming reference junction or cold junction is at 0°C.Table values are different for different thermocouple because thermoelectric properties are different for different metals
Compensating cables
Milli volts signal from thermocouple need to be carried to control panel input terminals . using ordinary copper cables is a bad idea . This is because ordinary cables wires are made with same metals and they doesn’t show thermocouple properties . it results formation of many thermocouple junction So measurement will become erroneous.Using true thermocouple metals throughout the length is the ideal case .But it is not economical .A method is using compensating cables .These are the cables which keeps the similar temperature EMF relationship as that of true thermocouple . Also they are cheaper .
Comparison -Thermocouple and RTD
Both thermocouple and RTD are used for temperature measurement .But they differ very much in many respects .
RTD are more accurate and are used for comparatively lower temperature ranges.For example pt100 RTD has its range between .-200 to 600°C.The metals changes resistance with temperature .This property of the metal is employed in temperature measurement using RTD.
RTD is a passive transducer .Means it doesn’t produce electric signal by its own .
.But Thermocouples have wide range for temperature measurement .But they have less accuracy compared to RTD .They are active transducers .They produce a millivolt signal .