DP Level Transmitter Range Calculation
Differential pressure transmitters are greatly employed in industries for the measuring hydrostatic pressure in a tank thereby finding the level. Range calculation of differential pressure transmitter is an important procedure in process level measurement applications .In this article we will learn the concepts of level measurement using Dp transmitter and DP level transmitter range calculation .
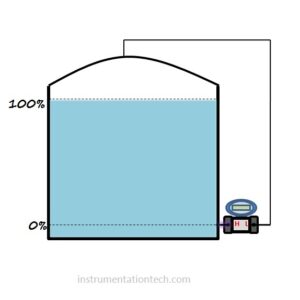
Suppose we have an application like tank level measurement.The liquid level in the tank has to be measured using Differential pressure transmitter.
What range should the transmitter have inorder to properly monitor the tank level ????
Or how to calculate the range for Dp transmitter for tank level measurement application .
What are the data we need for Dpt level range calculation. ?
Let’s go through some basic concepts of Dp type level transmitter range calculations

Hydrostatic method for Level Measurements
DP level transmitter range - selection
And we have to consider them.
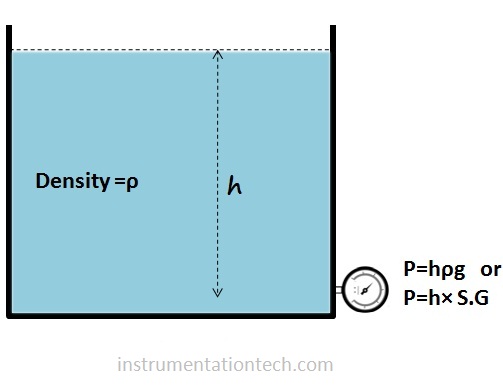
P = h × SG
Density/specific gravity of liquid in tank
Density liquid or its specific gravity both represents the same physical quantity.
Density
Density is a measure of how closely particles in matter is arranged.or it is the mass of substance in unit volume.
Density=Mass/volume
Density has units which in SI system expressed in kg/m³
Specific gravity
Density of liquid expressed relative to water density is the specific gravity of that liquid
S.G = Relative density
=density of liquid/density of water
Being a ratio specific gravity has no units.
Specific gravity should be non variant for hydrdrostatic type level measurement.
Hydrostatic type level measurement are applicable when the liquid keeps it’s density constant .Density should not be a varying one because a changing density makes level measurement incorrect
Why????
We know hydrostatic pressure at point due to a liquid of height h above is
minimum leve and maximum level??
0% and 100%
For calculating the range values LRV and URV of a transmitter,it is essential to know the position of required minimum level and maximum level.

MINIMUM LEVEL 0%
In many case it is very much close to the tank bottom.But in some cases the process or process philosophy prefer the minimum level some eights above bottom level due to various reasons . For example some mounting difficulties may force us to position the transmitter above the minimum level position .The transmitter should sent 0% signal or 4ma in this position .And in SCADA or HMI we can conveniently scale this 4ma as per the tank dimensions.
MAXIUMUM LEVEL 100%
At which height the transmitter should send 100% signal or 20ma. Or at which height of the tank is the required maximum level position.we need this position for transmitter s URV calculation

Open tank and closed tank connections
Measurement of level in open tank with Dp transmitter doesn’t require it’s LP side tapping connected to tank top.It is open to Atmosphere.The differential pressure is the difference in liquid head and atmospheric pressure.(Which is taken as zero in gauge scale.)so HP side pressure is the direct measure of level in the tank
CLOSED TANK
Why we are using DP transmitter and not using pressure transmitter for level measurements?
Incase of open tank .You can use pressure transmitter with proper range for the level measurements .But for closed tank you should use DP transmitter .And tapping from the tank top to the LP side is needed .The reason is below .
In closed tank there may be some vapour developed above the liquid surface or the tank itself may be a pressurized one like in boiler steam drum. A Dp transmitter connected to tank bottom will experience additional pressure in addition to the differential pressure due to liquid heads .This unknown extra pressure will cause error in the level measurement .To avoid this LP side is connected to the top of the tank.This method allows the unknown pressure above liquid surface simultaneously acting at both ports of DP transmitter thereby cancelling the effect.So the net differential pressure created in Dp is due to the height of liquid only.
Dry Leg and Wet leg
Dry leg connection means the leg or tapping connected to the LP side from tank top is not filled with any liquid or containing any condensate. So it is dry .only gas prassure is acting through this LP tapping to the transmitter.
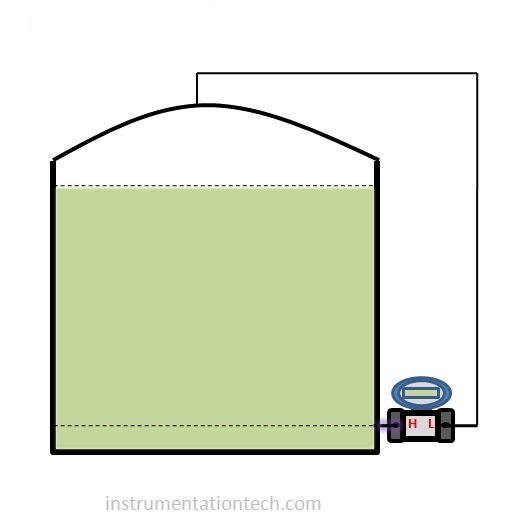
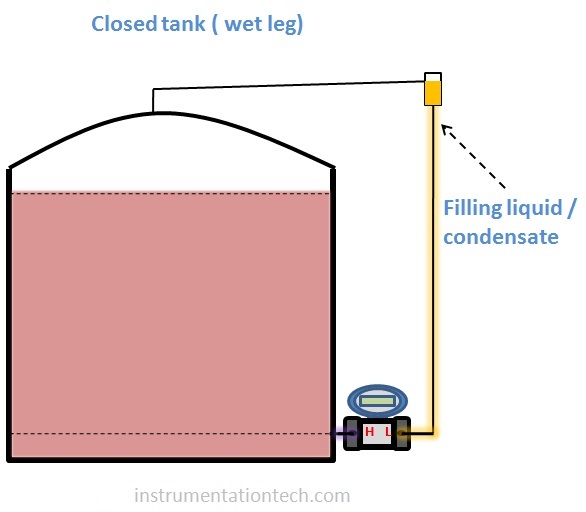
In closed tank wet leg connection the LP side tapping is filled with condensate or any other filling liquid.Filling liquid is used for the protection of transmitters from direct exposure of corrosive vapours or gas.
DP Transmitter Position
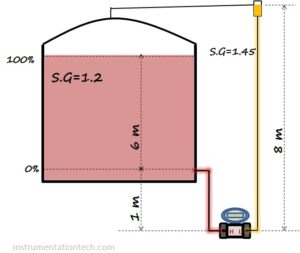
There are number of ways for mounting of Dp transmitters for level measurement .It is preferred to mount the transmitter at the minimum level position of the tank. But it is not possible always. May be some access problems to the transmitter or mounting or maintenance difficulties or some other reason forces us to mount the transmitter some heights below the minimum level position .This creates an extra head on the HP side of the transmitter. We have to consider these height because when the level is at 0% the impulse tube is not empty .It is filled with the process liquid and a head pressure equivalent to that height is acting on the HP side .so at 0% the Dp is not zero .This extra head is present throughout the range 0-100%.we need to consider this extra head in level range calculations.
Ideal case no suppression.
Transmitter is mounted at the same level as tank minimum level.There is no head pressure acting on the transmitter when the level is at 0%.So the transmitter’s lower range value is zero in any units in this case . Transmitter can be calibrated with
LRV=0 ,. URV = h×S.G
Transmitter below minimum level (Zero suppression)
The transmitter is mounted some heights below the minimum level position
When the level is at 0% head pressure acting on the HP side is not zero as in the ideal case discussed above.This is because the impulse tube is always filled with the liquid .A liquid head pressure equivalent to the height of liquid in the impulse tube is always acting on the HP side causing a head pressure in addition to head corresponds to the level in the tank. .This head depends on the height of minimum level position from the transmitter connection port .
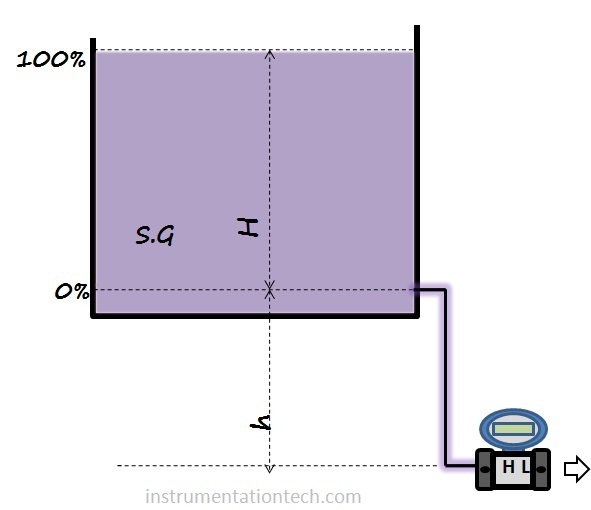
If we use a transmitter which is calibrated considering only the height between tank minimum level and tank maximum level then transmitter output will be greater than 4ma at 0% and greater than 20ma at 100%. This is because of the extra head created in addition to the liquid level in the tank .The extra head is developed because the transmitter is mounted some heights below the tank minimum level and head equivalent to the liquid in the tube is always present in addition to the liquid in the tank. It is always present even if the level in tank is at 0% .so the transmitter have to be properly calibrated or the extra head pressure have to be suppressed to get the transmitter output proportional to the level in the tank (4ma at 0% and 20ma at 100%) This procedure is called zero suppression.
In older pneumatic transmitters there is a setup provided for achieving this zero suppression called suppression kit. And in modern electronic transmitters we only rerange or properly calibrate the transmitters by considering all the head pressure for calculating LRV and URV..
In te figure shown we are measuring tank level between 0% and 100%.suppose h is the height of liquid in the tank from 0% position.
Let the height of minimum level position to transmitters HP port be H .
So head pressure acting on DP transmitter is
H×S.G+h×S.G
But we need only the term H×S.G as it corresponds to the measuring span . The head h×S.G should be suppressed .The procedure of suppressing this extra head created when minimum level position is some height above the transmitter port is called zero suppression.
in the example given in figure LRV and URV can be calculated as follows
LRV=DP at 0%
= h×S.G – 0
LRV = hxS. G
URV=DP at 100%
DP = HP-LP
= (H+h)×S.G – 0
=(H+h)×S.G
That is URV =(H+h)×S.G

Zero elevation
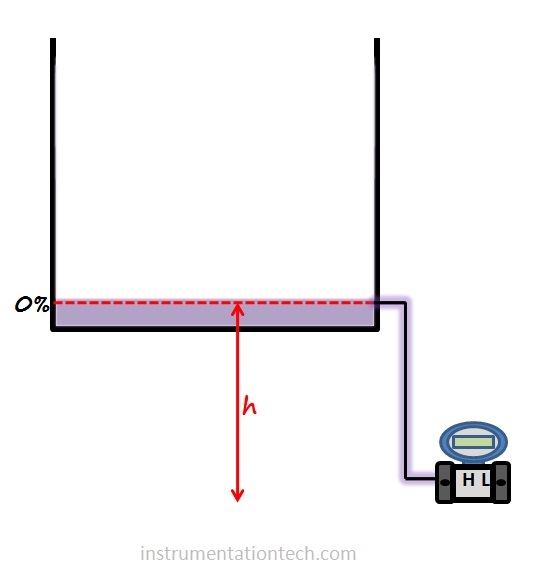
In closed tank level measurement using Dp transmitter as discussed earlier there will be filling liquid or condensate liquid in LP side impulse tapping.These condensate or filling liquid is always present in the LP side tapping and we should consider these liquid for transmitter range calculations as it is a permanent head on LP side.
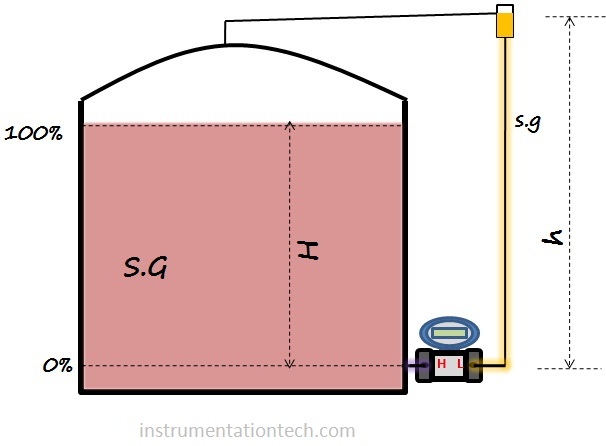
Let us evaluate the head pressure acting at when the tank level is minimum.
At 0% level,
pressure on HP side = 0
Pressure on LP side = height of liquid filled×S.G of filling liquid
So LP side pressure is more and DP is negative at 0%
So this negative DP should be interpreted as 0% .If e are using a transmitter which is calibrated considering only the head due to the liquid in the tank(as in the ideal case) then Transmitters output will be less than 4ma at 0% and less than 20ma at 100%. This is because the condensate or filling liquid in LP side tube makes the differential pressure a lesser value .So in order to properly transmitting the level (4ma for 0% and 20ma for 100% )we need to elevate the LRV and URV and the procedure is called zero elevation
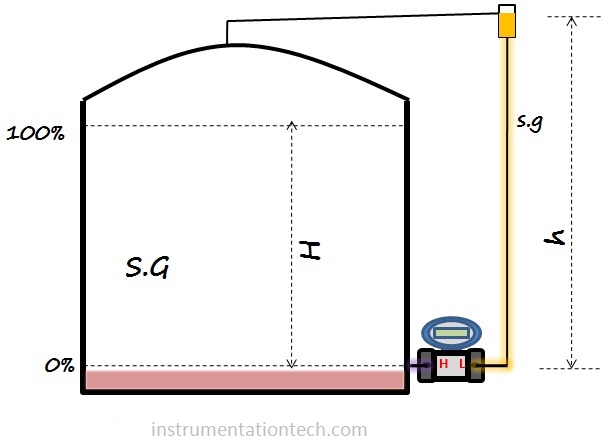
On examining we can calculate LRV and URV as
LRV=DP at 0%
=Hp-LP
=0 – h×s.g

URV= DP at 100%
=H×S.G- h×s.g
So the LRV calculated is negative and URV may or may not be negative( depends on the heights and specific gravity of filling liquid and liquid in tank).Also we can see that LRV and URV is reduced by a value of h×s.g when comparing it with ideal case.(no filling liquid in LP side).
Calculation
DP=HP-LP
In short to calculate range for a level transmitter remember these points .
For calculating pressure acting at HP side and LP side use equation h×SG.
1.calculate Dp at 0% which is LRV
2 .Calculate DP at 100% Which is URV
3 .DP=HP-LP
4.For calculating HP and LP use equation P=h×S .G